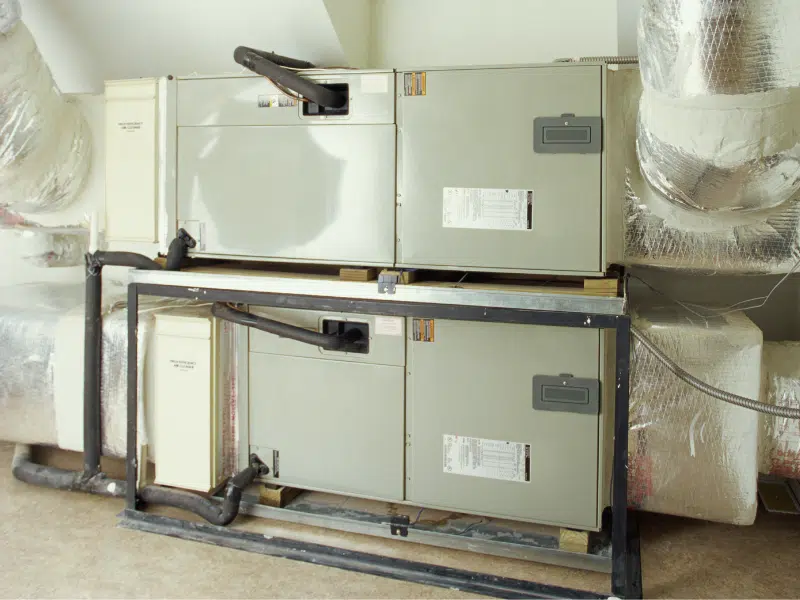
Do you need a new heating system? How do you identify the best furnace to keep your home comfortable throughout the cold season? While this can often be a challenge for homeowners, it doesn’t have to be.
When buying a new furnace, in addition to the cost of the furnace itself, you should also note what the AFUE ratings are. When furnace shopping, you’ve probably come across that glaring yellow Energy Guide label on every system.
But do you know what those readings mean? Are you able to choose the best furnace for your home based on these ratings? If not, don’t worry; we’ve created this guide to help you out.
What is AFUE Rating?
AFUE (Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency) is a measure of how much fuel an appliance uses against how much energy it generates.
These ratings are commonly used to determine energy efficiency in gas furnaces, so you can avoid choosing a heating system that pokes holes in your pockets with each energy bill. In other words, furnace AFUE ratings help you to determine the amount of fuel the furnace can convert into heat.
The higher your furnace’s Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating is, the better. It means that the unit uses most of the energy it consumes to generate heat.
Example:
Say you have two gas furnaces, one with an AFUE rating of 85%, while the other one has a 95% AFUE rating. These ratings indicate that the first furnace converts 85% of the fuel energy into heat, while the second one can convert up to 95%. In this example, the second furnace is more energy efficient than the first one.
Now assume the fuel for each furnace was worth $150 in each of the furnaces. How much do you save with the more efficient unit?
If you put $150 worth of fuel in the first furnace with 85% efficiency, it means that $127.50 will be converted to heat while $24.50 is wasted. The second furnace, on the other hand, will generate heat worth $142.50, and only $7.50 is unused. Comparing the two units, the second one allows you to save $17 more for each $150 worth of fuel used.
Gas Furnace AFUE Ratings
A few decades ago, the average AFUE rating for gas furnaces was 50%. However, this has significantly changed with time as technology has advanced.
Currently, most gas furnace AFUE ratings range above 90%, which makes them highly energy efficient. This average is typically measured on an annual basis, hence why it is called the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency rating.
According to the Department of Energy requirements, furnaces should have a minimum AFUE rating of 80%. This way, the furnace turns 80% of fuel energy into heat energy. The 20% difference is allowed since some energy might be lost through leaks, furnace inefficiencies, or other factors, especially as the furnace ages.
Are AFUE Ratings for Gas and Electric Furnaces the Same?
No, electric furnaces are much more efficient. The average AFUE rating of gas furnaces can go way over 90%, while electric furnaces have an AFUE rating of 100%. This means that no fuel energy is lost when converting to heat energy.
But how? Usually, electric furnaces heat your home through electric resistance heating. As such, this system has no exhaust, and it can convert all the electric energy into heat energy. That’s the reason why electric furnaces have 100% AFUE ratings.
But does this make electric furnaces better than gas furnaces? Not entirely! While an electric furnace will save you energy, the cost of buying an electric furnace is way higher. And with the rising costs of electricity, electric furnaces could become more expensive to operate as well.
Therefore, before making that final purchase decision, ensure that you consider all the factors. Seek the professional advice of an HVAC technician to ensure you buy the best furnace for your home.
Calculating AFUE Ratings
Now that we’ve covered AFUE ratings, you may wonder how they are calculated. When calculating the AFUE ratings of a furnace, we must first know the amount of energy contained in different types of fuel.
A quick recall to science class: energy is measured in kilojoules or kJ.
If you are using natural gas, you will have 36,000kJ of energy for every cubic meter of fuel. Or, if your furnace uses oil, a barrel of oil contains 6,120,000kJ of energy.
These two figures mean that a gas or oil-powered furnace with a 100% efficiency will produce 36,000kJ and 6,120,000kJ of energy, respectively. But since these furnaces aren’t 100%, the amount of energy produced will be less.
The general formula here is as follows:
Energy Output = AFUE Rating x Energy Input
Therefore, for a gas furnace with a 90% AFUE rating, the calculations will be as follows;
Energy Output = 90/100 x 36,000kJ
The energy produced from the gas furnace will be 32,400kJ for every cubic meter of natural gas.
For an oil furnace with the same AFUE ratings, the calculations will be:
Energy Output = 90/100 x 6,120,000kJ = 5,508,00kJ.
This means the furnace is producing 5,508,00kJ of energy for every barrel of oil.
Other Factors that you Should Consider when Purchasing a Furnace
Furnace AFUE ratings are not the sole determinant of a quality HVAC system for your home. After you’ve identified the best ratings, you should also consider the following factors:
Cost
Cost is often a factor when purchasing anything. However, when you’re furnace shopping, be wary of being too focused on cost. While it is wise to stick to your budget, also ensure that the furnace you buy is sufficient to heat your home and that it will not break down in just a few years. Remember, cheap can be very expensive.
Also, remember to include maintenance costs when budgeting for your HVAC system. Routine maintenance will ensure that your unit lasts long and heats the home effectively.
Capacity
Depending on how large your living space is and the heating requirements, ensure that you choose a unit that effectively heats up your indoors. You can only guarantee this by choosing a furnace that will produce enough BTUs – or British Thermal Units. This is a unit of measurement used to determine if a system is strong enough to supply heat to your space effectively.
Let an expert help you with this task.
Conclusion
If you’re a new homeowner, or a seasoned homeowner who needs a new HVAC system, don’t worry, you don’t need to commit all of this to memory.
If you need help with maintaining your furnace or figuring out your system’s efficiency ratings, contact a reliable HVAC contractor today.